Import from Roboflow Universe
Download or clone images from Roboflow Universe for use in your projects.
Roboflow Universe hosts open-source datasets and pre-trained models for computer vision. Over 200,000 Datasets and 50,000 pre-trained models are available. There are two methods to adding Universe images to your dataset. You can download the entire dataset or clone select images from Roboflow Universe for use in your projects.
Download a Full Dataset
First, find a dataset on Roboflow Universe. Then, click the Download Dataset button. A pop up will appear asking you in what format you want to export your data. The options displayed are formats compatible with the computer vision task the model solves (object detection, classification, segmentation).

You can either download your dataset directly from Roboflow Universe by exporting a ZIP file or you can retrieve a code snippet that you can use to download a dataset. The provided code snippets may be useful if you are using the dataset in a notebook.
Clone Images to Your Roboflow Project
Once you have created a new Project in your Roboflow account, head to Roboflow Universe and use Dataset Search to find projects with images that will work for your use case.
When you find a Project with images and/or annotations that work for you, open the Images page and select images to clone. You can select individual images by mousing over the image and clicking the checkbox in the upper right corner of the image. To bulk add images, you can click Select All to clone all images visible in the current results page.
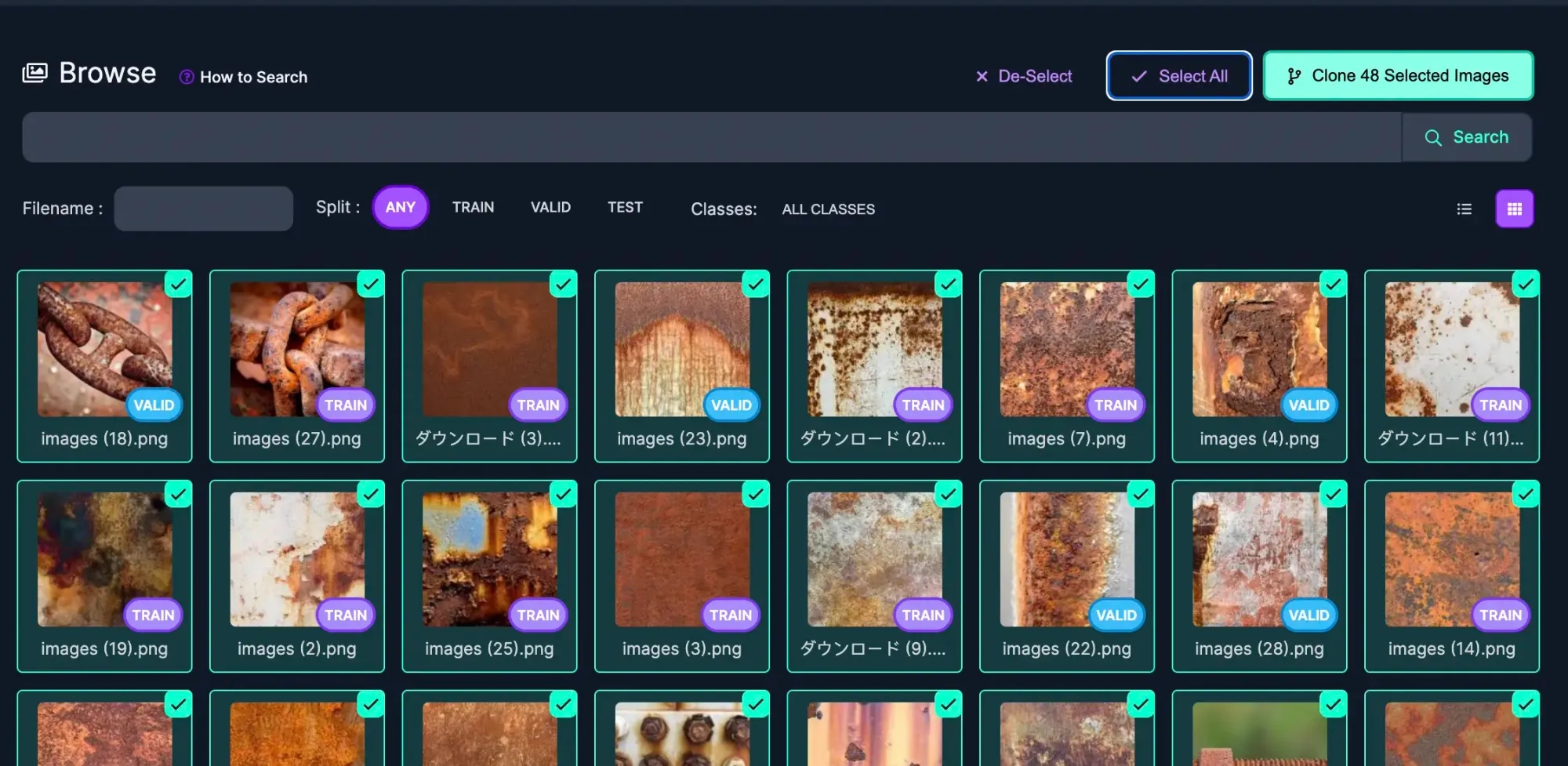
After selecting images you want to clone into your project, click Clone Images and choose the Workspace that contains the Project.
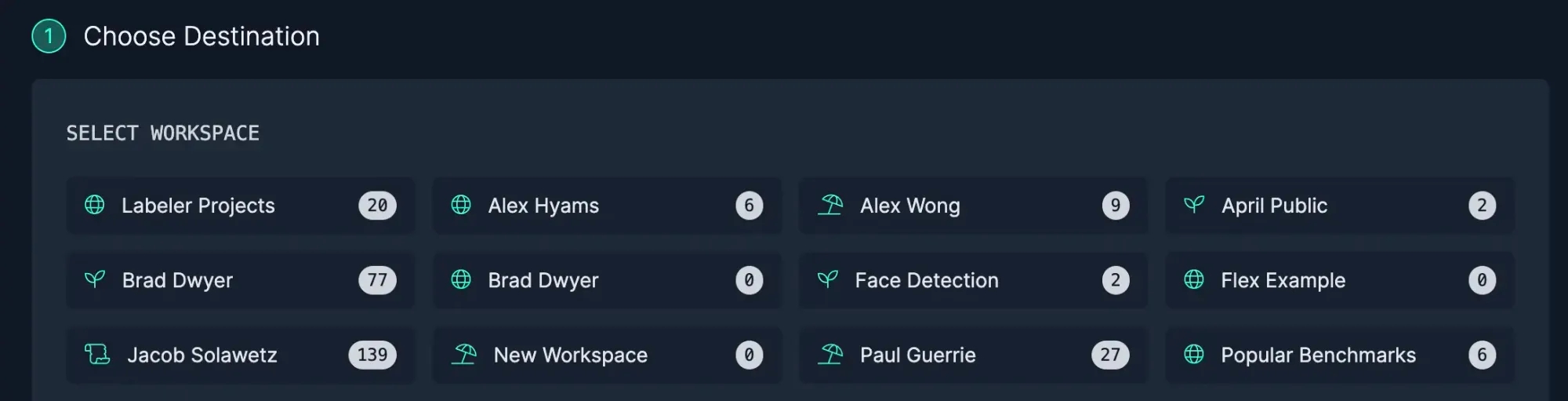
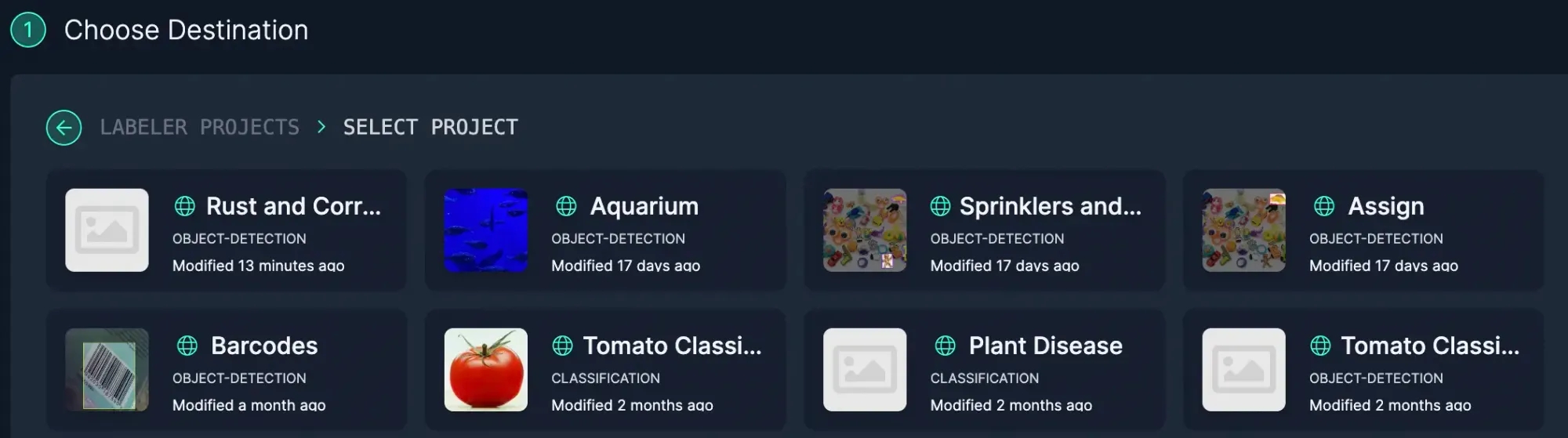
Select the Workspace and then choose the Project to add the images to the Dataset.
When cloning the images into your Project, you can import the images with, or without, the annotations. As you clone images into your dataset, images with augmentations will not be included and you'll be able to apply your own augmentations when you generate a dataset.
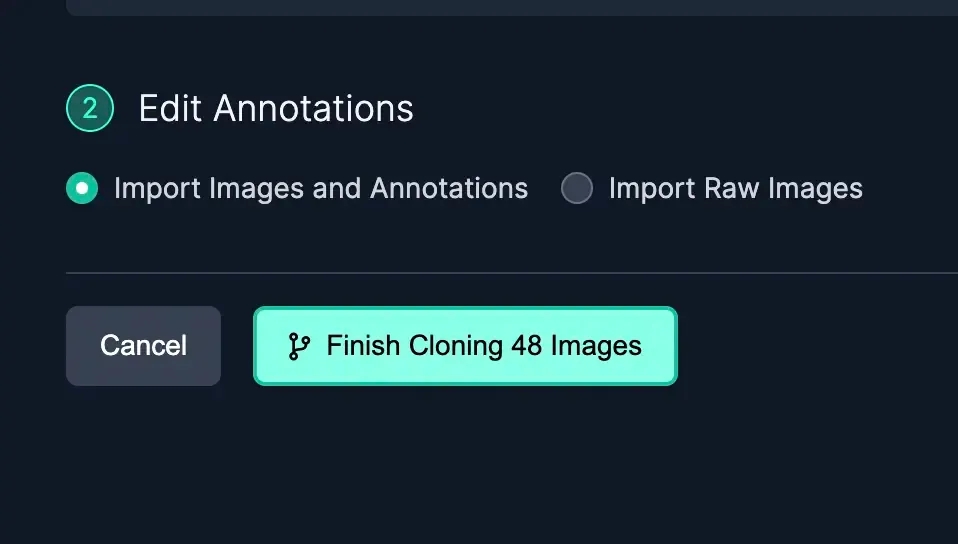
Importing raw images (images without annotations) is a helpful option when:
You find images that contain the object you're interested in but the annotations may not be focused on the object you plan to train your model to identify
You find a classification dataset but your project requires bounding boxes
You want to use polygon annotations but the project has bounding boxes
Roboflow will check if you're attempting to add images that already exist. Don't worry: You won't be able to add duplicate images.
Advanced Tips to Find the Data You Need
Use Dataset Search to find exactly the data you need to fine tune your model. As an example, if our rust detection model was struggling with detecting rust on pipes, we will want to find more images of pipes to add the dataset. Rich semantic search in Projects and broadly in Roboflow Universe can be used to find the niche data you need.
Using Dataset Search within research datasets can help you quickly collect a high number of fairly well labeled data to help kickstart a model.
Another way to find specific data is by using the Health Check page and clicking on a specific class. This will bring you to the Images page with that class filtered to the top of the results.
If you can't find the data you need in Roboflow Universe, you can always upload your own data via API or use YouTube videos as training data.
Last updated
Was this helpful?